WWII: Italian Invasion and Roman Resistance
I spent March 17th and 18th traveling around Rome and western Italy learning about Italy’s role in the Second World War. I discovered that during the war, Rome and the rest of the country played key roles for both the Allied and Axis powers. Lead by a JFRC teacher, SLA, and JFRC alumni Phil O’Connor and Jim Centner, the trip was extremely educational and fun. I was hesitant to go at first. I wasn’t sure if it would be worth the money (€ 50) or the time, and I had no particular interest in talking about a war that I had already studied in high school. I figured I knew the history, and the trip would not be anything new. I am happy to report that I was wrong in every way. Not only was the trip worth every penny, it taught me a ton about the war and 20th century Italian culture.
On the first day, we bussed around Rome, visiting historic sights at which major events took place during the Nazi occupation of Rome. First, we walked down Via Rasella, the steep and narrow street where, on March 23, 1944, a group of 16 members of a communist resistance group The Gruppo d’Azione Patriottica (Patriotic Action Group) attacked a column of SS police as they carried out their routine march through the streets. The attackers used an improvised bomb made of 40 pounds of TNT encased in metal and hidden in the bottom of a garbage cart. As the column of soldiers approached, the man pushing the cart lit the fuse on the TNT. The explosion killed 28 SS policemen and may have killed two civilian bystanders as well. When the bomb went off, the soldiers, confused and alarmed, began firing their weapons into the apartment windows above them. They thought that the bomb had been dropped onto them from above. Civilians near the windows were killed and the street was a scene of chaos as everyone panicked.
Following the attack, Hitler ordered a reprisal as punishment for the killing of his policemen. Nazi leaders agreed on a reprisal of ten Italians for every one German soldier. In the end, 335 Italians were killed as punishment for the deaths of 30 SS policemen. The 5 extra people were killed to keep them from disclosing the location of the massacre. You can read about the Ardeatine Massacre online, so I’ll spare you the details. I learned that reprisals like this one were common among opposing groups during the war. I spent the day wondering how and why people continue to do these things to one another. The area is now a cemetery for people killed in the massacre.
From there, the day became a little more cheerful. We visited the Liberation Museum in Rome. It had been a prison where some of the victims of the Ardeatine Massacre were kept, but since the 1950s it has been a museum celebrating April 25th, in 1945 when Italy was liberated from Nazi rule.
Day Two started at 7 AM. We hopped on the bus and visited a large German cemetery. It was pouring rain so our visit was short. The cemetery was perfectly symmetrical with plain white crosses at each grave. Each gravestone marked the place of at least 6 German soldiers. Typical Nazi resourcefulness. As the rain cleared up, we made our way to my favorite place of the trip, Piana delle Orme, a huge WWII museum and park. We spent two or three hours at this museum, walking through the giant hangars full of jeeps and tanks used in the war, depictions of battle scenes, and iconic cultural items of the time. Many of the rooms used mannequins and models to create scenes of big events during the war. Several exhibits had red buttons that, when pressed, would play music and sounds of explosions and battle commands that enhanced the experience of each scene. Here I enjoyed walking around at my own pace, reflecting on each room as I tried to take in all the information. Before this trip, I didn’t know how important the invasion of Sicily had been. I had never thought about the combat that took place in North Africa. It’s hard to explain through this blog, but I felt connected to the time period more than I ever did before.
For whatever reason, the museum also had several exotic animals like peacocks and black swans called Cigno in Italian. The grounds were lined with palm trees and small streams. At one end there was a landing strip with several WWII planes and jets. After all of the death and sadness of the first day, the museum offered another look at 1940s Italy. Of course, we were still learning about the war, but the museum’s displays somehow made it all seem a little less grim. I left feeling proud and in awe of the sacrifices made by everyone who lived during the war, on and off the battlefields.
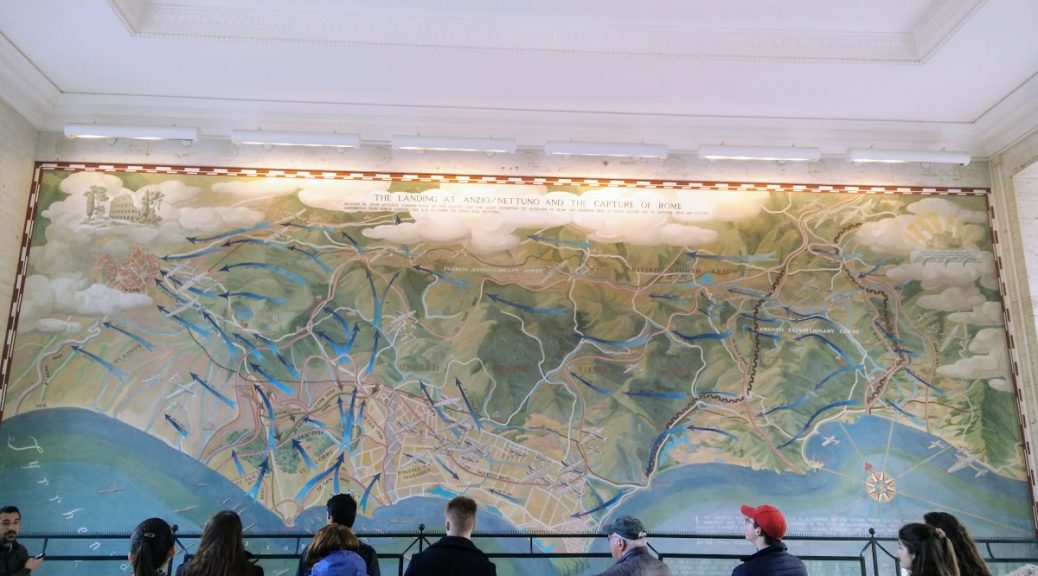
We visited The Sicily-Rome American Cemetery and Memorial next, which was infinitely more beautiful than the German one from that morning. Nothing against German cemetery design, but we definitely did a better job here. The grounds were made of sprawling green lawns with a fountain in the middle. It didn’t hurt that the sun was shining and a light rain left a rainbow hanging over the Italian cypress trees. Adjacent to the graves is a building and memorial with paintings depicting the Allies routes as they fought their way up through Italy. We stopped in to hear more about the efforts to liberate Rome from the axis powers and took a group picture. Before we left, we visited a few graves. One was that of Ellen Ainsworth, a nurse who was awarded the silver star for her bravery.
The weekend was packed full of walking, learning, propaganda posters, 1940s music, pizza and beer, some sorrow, and more walking. Every time we talked about a tragic event from the war, something beautiful was there to remind us that life goes on. For any future JFRC students that managed to read this whole article, I highly recommend being a part of the WWII trip.